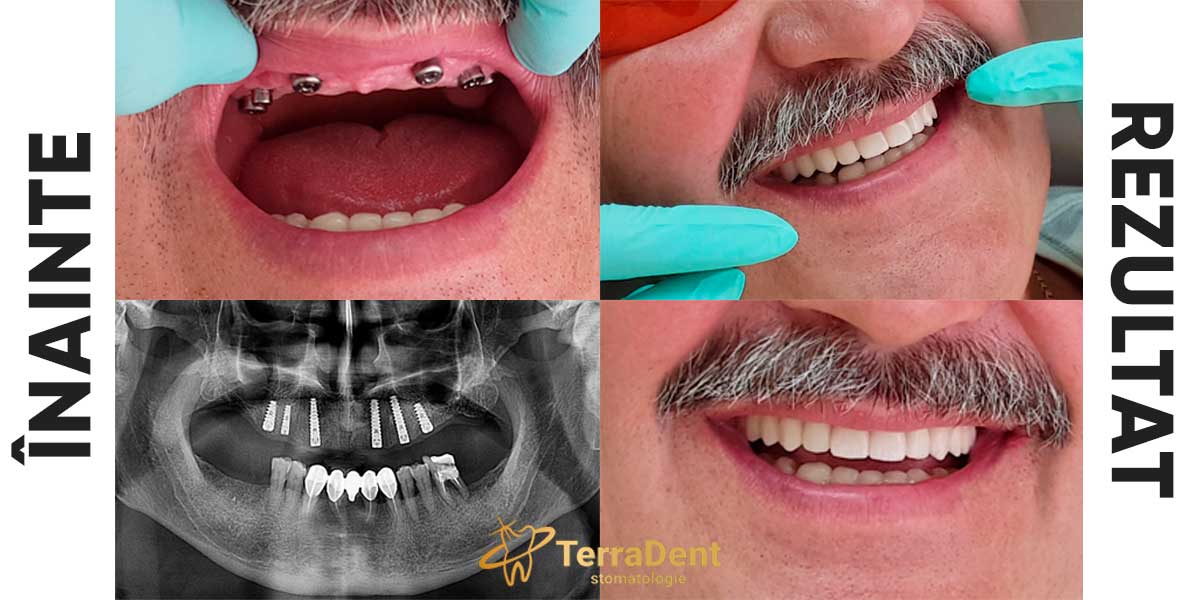
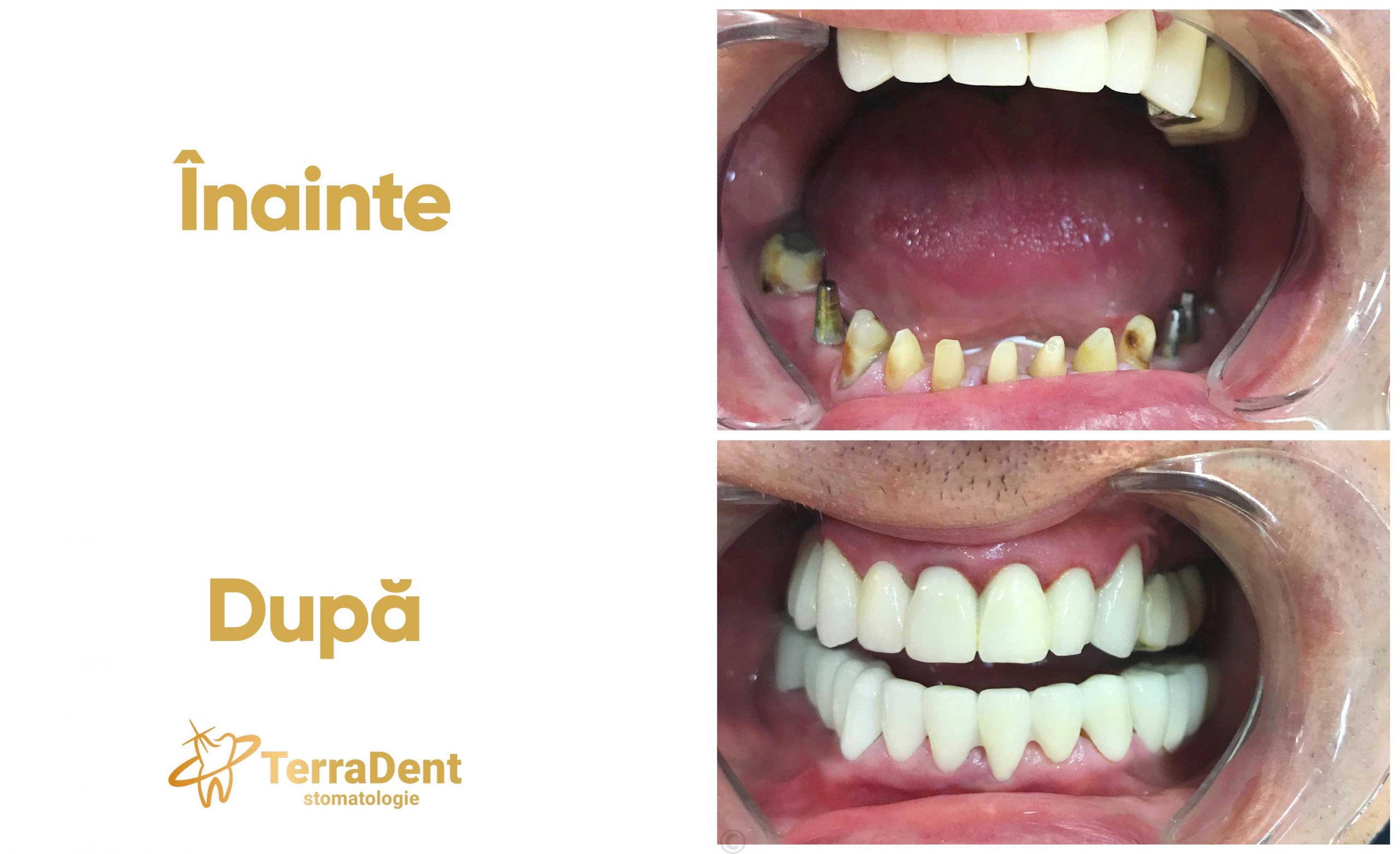
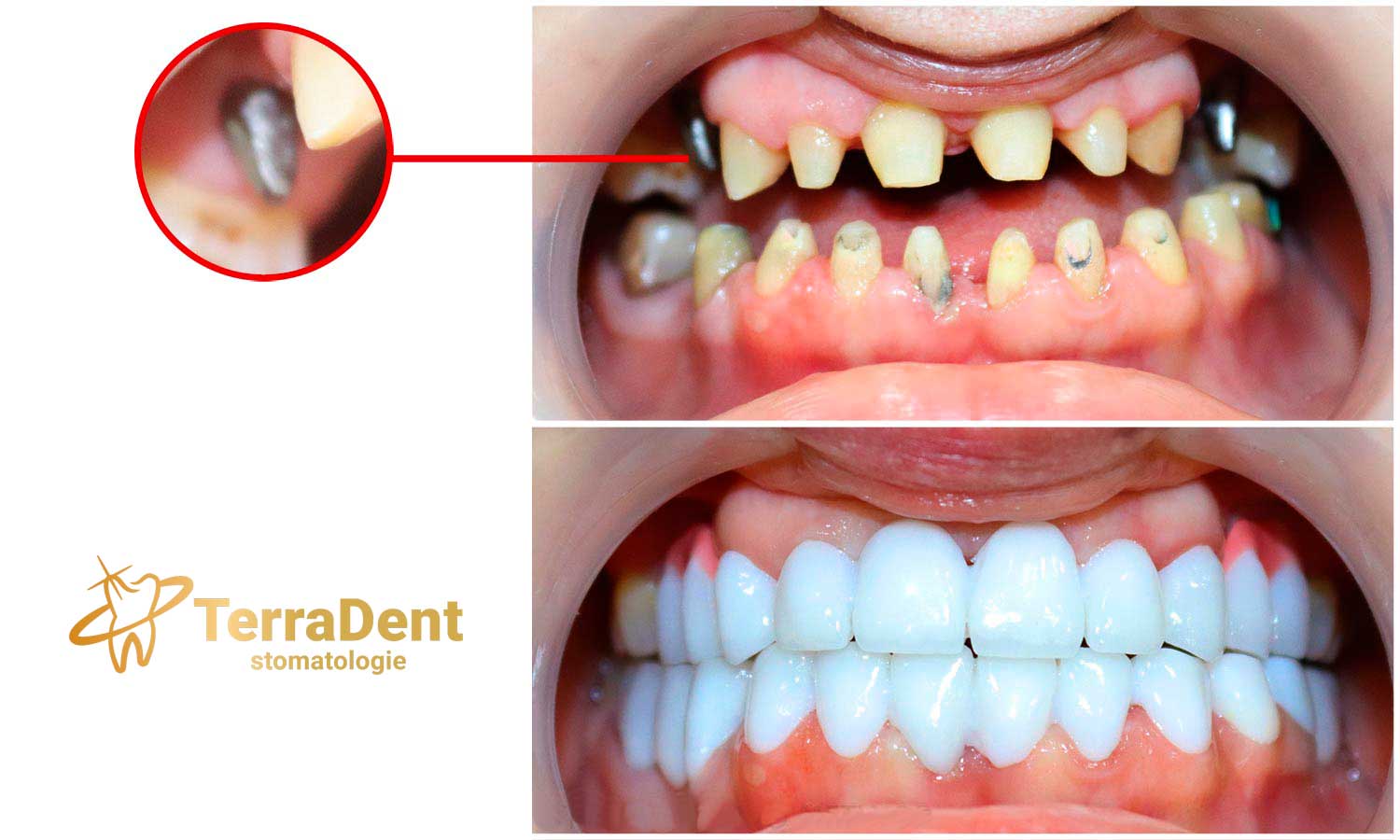
The dental implant is the artificial, natural-looking substitute for the root of a missing tooth that provides the same function and behaves identically to the structure of its root.
What is a dental implant?
The dental implant is the artificial, natural-looking substitute for the root of a missing tooth that provides the same function and behaves identically to the structure of its root.
From a structural point of view, the dental implant is a piece of pure titanium provided with coils, most often in the form of a screw.
Its insertion is made following a tooth extraction after the place has healed or, as the case may be, in the same session with the extraction.
Reasons for choosing dental implants as an oral rehabilitation treatment:
Replacement of one or more irrecoverable or missing teeth;
Restoring the stability of crowns or bridges;
Increasing the support and stability of the denture;
Preventing the appearance of gastric problems by increasing the chewing comfort of food;
Cleaning neighboring natural teeth – does not require sanding neighboring natural teeth as in the case of dental bridges and prevent the anchoring of mobile partial dentures;
Keeping the volume and density of the maxillary bone unaltered – provides beneficial stimuli to the bone as well as the roots of natural teeth;
Removing smile inhibitions, contributing to correct diction and implicitly improving speech;